Mirroring what is happening in the world, there is an Islamic revival in the Caucasus and Central Asia, with all that it means for local Christians.
The predominantly Muslim Central Asian Republics, after the collapse of the Soviet Union of which they were part, have seen an increase in the persecution of Christians. The fall of dictatorship, in a pattern similar to that of post-war Iraq and the “Arab Spring” in Egypt, Tunisia and Libya, seems to have “liberated” the radical elements within the Muslim communities.
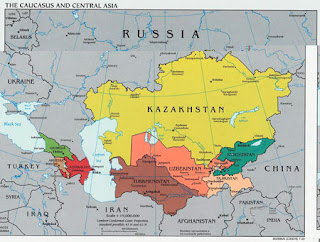
The now independent countries of Central Asia are the following five, in order of population size: Uzbekistan (just under 30 million people), Kazakhstan (16-17 million), Tajikistan (7-8 million), Kyrgyzstan (5-6 million), which is particularly topical now because it is where the family of the Boston bombings suspects lived for a time, and Turkmenistan (just over 5 million), for a total population of 64.7 million in 2012, the vast majority of whom are Muslim. Another Muslim-majority country that was part of the Soviet Union is the Republic of Azerbaijan, the largest in the Caucasus, at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, with a population of over 9 million, 95 percent of whom are Muslim.
What is paradoxical is that, while during the Soviet era the ruling Communist Party, through the education system and official propaganda, imposed so-called "scientific atheism" (a name reminiscent of so many Western atheists who, à la Richard Dawkins, fallaciously declare the denial of God to derive from science), for Christians in Central Asia and the Caucasus the end of the Communist regime, which was supposed to bring freedom of religion among other freedoms, brought instead another form of religious oppression.
It may have freed Christianity but, by freeing Islam as well, it unleashed hostility against Christianity, from governments as well. Churches are raided, closed and torched, crosses are burnt, fathers are arrested and fined for holding a prayer meeting and religious leaders for not registering the church (while at the same time the strict legislation makes it impossible for churches to register), believers are beaten up during raids on their homes, Christian literature is destroyed, and families are restricted to owning only one Bible. There is growing intolerance, and the media target organizations and beliefs.
The organization Russian Ministries' Facebook page says: "However due to the strictness of the laws in these countries, it is practically impossible for churches to register and practically all religious materials are illegal, meaning that it is becoming more or less de facto illegal to practice Christianity".
It does not end there. In Azerbaijan "The government is also intent on vilifying Christians to the public. Government-controlled mass media accuses believers of occult practices, hypnosis, and extremism, while newspaper articles encourage discrimination and physical abuse of Christians and other minorities".
In the article Central Asia: Growing Religion Oppression, Anneta Vyssotskaia, of the World Evangelical Alliance Religious Liberty Commission, writes:
During 2007 there were numerous reports of restriction and persecution of Christians in Central Asia. However, these may be only the tip of the iceberg of the real situation regarding persecution of the Christians living and worshipping God in the predominantly Islamic environment. Most of what would be considered persecution in Western countries is just part of daily life for every Christian there; persecution comes from family, neighbours, Muslim religious leaders and the government. Most of these cases may never become generally known. Religious legislation in these countries is undergoing changes that restrict worship and evangelism even more. Despite this, the number of Christians is constantly growing.
In Uzbekistan a small Baptist church which has endured more than a decade of official harassment was again raided during Sunday morning worship on 24 March. "The secret police officer who led the raid told the Baptists that 'all believers are backward-looking fanatics who drag society down'". This pronouncement again rings a bell to Western ears. Take away the raid and you can hear our own "progressives" and "enlightened" gay-marriage supporters saying very much the same.
In its survey analysis of freedom of religion or belief in Kazakhstan, Forum 18 News Service found serious, continuing violations of human rights, including:
attacks on religious freedom by officials ranging from President Nursultan Nazarbaev down to local officials; literature censorship; state-sponsored encouragement of religious intolerance; legal restrictions on freedom of religion or belief; raids, interrogations, threats and fines affecting both registered and unregistered religious communities and individuals; unfair trials; the jailing of a few particularly disfavoured religious believers; restrictions on the social and charitable work of religious communities; close police and KNB secret police surveillance of religious communities; and attempts to deprive religious communities of their property. These violations interlock with violations of other fundamental human rights, such as freedom of expression and of association.
And it is getting worse. In Kazakhstan, a proposed new Criminal Code expected to be approved by the government in May and presented to parliament in July, if adopted in its current form, would allow those who lead unregistered religious communities to be imprisoned for up to three months, and those who share their faith for up to four months.
Perhaps for the first time since Kazakhstan gained independence in 1991, a court ordered religious literature to be destroyed, in the form of 121 Christian books confiscated from a believer who was handing them out on the city streets when police arrested him. He was given a fine corresponding to a month’s wages.
In recent weeks and months there have been many incidents in which Central Asian churches have been raided, often without warrant, and, if Christian literature or an on-going service were found, church members were given a heavy fine (in some cases as much as 100 times the monthly minimum wage) for possession of illegal material or unregistered religious activity.
To counter this worsening situation, on February 6 in Washington, DC Russian Ministries organized a briefing to raise awareness of the worrying trend among U.S. leaders, which was attended by 90 people, including people from the State Department.
The goal was to mobilize and get support from the global community to develop policies and put pressure on the governments of the Muslim former Soviet republics so that they give more freedom to the churches and leaders there.
Among the causes of suppression of religious freedom there appear to be both blasphemy laws and laws intended to combat religious extremism and terrorism, which seem to mistakenly conflate militant Islam and Christianity, as is the case of the new law introduced in Kazakhstan in late 2011.
In that country, with the declared intention to stamp out Islamic extremism and “to counter manifestations of religious extremism and terrorism”, Christians and other innocent faith minorities have increasingly become victims of the reform, aggressively implemented: after a year, among other abuses, 579 religious communities had been stripped of their registration rights.
Therefore Christians suffer from the presence of Islam in two ways: directly, through the various torching of churches, burning of crosses, attacks on apostates and the usual niceties, and indirectly, for becoming scapegoats of Islamic radicalism.
Anneta Vyssotskaia explains:
As religious liberty for churches in Central Asia deteriorates, some common trends are evident. Governments are increasingly negative about Christian outreach, especially amongst the Muslim population, and want to control it more or stop it completely.Sergey Rakhuba, President of Russian Ministries, an expert on mission issues related to Russia and the former Soviet Union, says in the above video: "In the 'stan' countries you cannot bring Bibles, you cannot bring literature, you cannot evangelize or share your faith outside of your home; but, in the case of Uzbekistan, you cannot even share your faith with your children, you cannot pray, and a meeting of more than 3 people is considered a violation of this law, and that's why people suffer and get imprisoned".
They fear tensions may escalate where the number of Christian converts in the local population is growing. In other instances governments legislate to control minority religious bodies due to concerns about the activities of Islamic groups. However as Christians are a religious minority throughout Central Asia they are restricted by such laws along with these Islamic and other minority religious groups. In addition local Muslim communities regard Muslim converts to Christianity as 'traitors' and enemies and persecute them in various ways.
Mission Network News reports:
It's like going back to the days of the cold war, he [Sergey Rakhuba] says. "Evangelical churches are not allowed to do anything outside of their homes, even inside their homes. If they gather together for prayer meetings they are punished and are penalized. Many pastors have already been thrown into prison there."In parallel with what happens in the Arab countries, we see in Central Asia the Christian communities targeted on two fronts: attacked by Muslim mobs, neighbours and leaders on one hand, and attacked or not protected by governments, police/army and local officials on the other.
While it's reminiscent of the days of communism, Rakhuba says, "This is a new wave of persecution that's based on radical Islamism, on nationalism, and even mainline churches like the Orthodox church...is the reason for persecution of local believers in Russia and Ukraine or other Slavic countries."
The information presented will help create a policy guide for Christians in the region to help fight laws that are meant to fight terrorism. "Based on those laws, evangelical Christians--for their most humble actions--are punished just for having prayer in their own home. So, we'd like to create some policies and to encourage governments to change it."
While the motivations of the former are the same (Muslims being Muslim), the reasons behind the latter may have less to do with Islam than in the Arab world. Kazakhstan’s 1995 constitution, for example, stipulates that it is a secular state, and the governments of the Central Asian republics are wary of theocracy and Islam in the political sphere, although Islamization in the region is increasing.
To help or contact Russian Ministries, visit http://www.russian-ministries.org/ or http://www.mnnonline.org/groups/RMI
